Dental cavities, also known as dental caries or simply “cavities,” are a common oral health issue that affects people of all ages. In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into various aspects of cavities and dental caries, addressing your questions and providing valuable insights into their causes, prevention, and treatment.
What Are Cavities and Dental Caries?
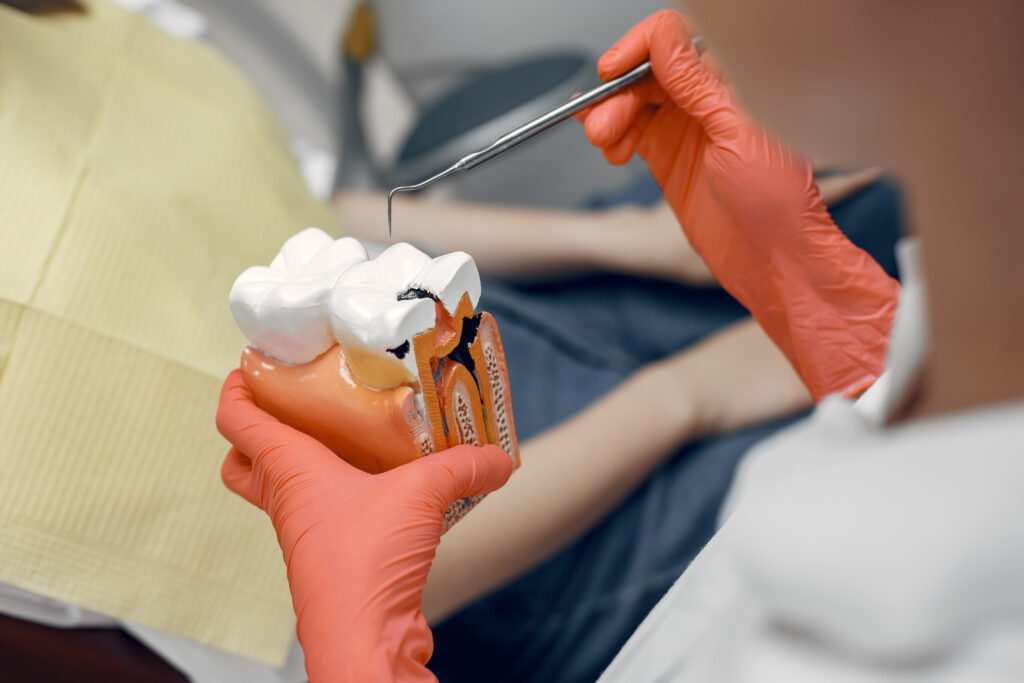
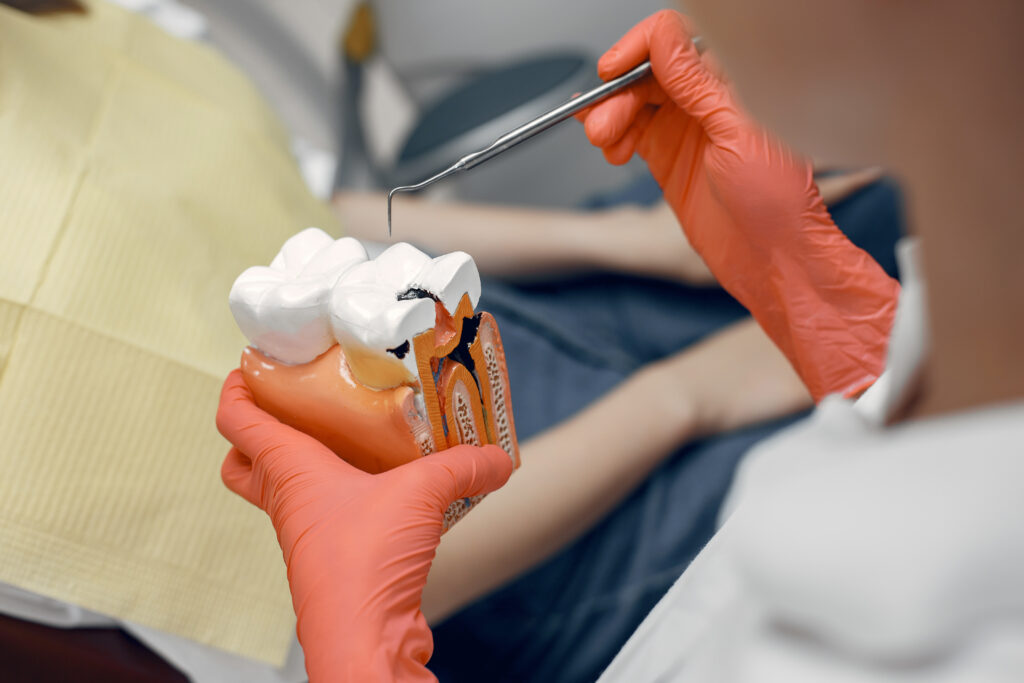
Cavities, scientifically known as dental caries, are areas of tooth decay or damage that occur when tooth enamel is eroded by acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. These small holes can become larger over time if not properly addressed. Understanding the causes and progression of cavities is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Can Cavities Be Reversed or Healed on Their Own?
Once cavities have formed, they cannot be reversed or healed on their own. However, in their early stages, cavities can be halted or remineralized through the use of fluoride treatments and good oral hygiene practices. Fluoride helps to strengthen tooth enamel and can repair minor enamel damage.
Can Cavities Cause Various Symptoms?
While cavities themselves do not directly cause headaches or other systemic symptoms, they can lead to localized discomfort and associated problems. As cavities progress, they may result in tooth pain, sensitivity, and, in severe cases, dental infections. These infections can lead to jaw pain, ear pain, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and a sore throat.
Can Cavities Spread or Be Contagious?
Cavities can spread within the mouth if left untreated. The bacteria responsible for cavity formation can be transmitted through activities like sharing utensils, kissing, or close contact. While cavities themselves are not contagious, poor oral hygiene and shared oral bacteria can increase the risk of cavity development in others.
Genetics and Cavities
Genetics can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to cavities. Some people may have genetic factors that affect the composition of their saliva and the structure of their teeth, making them more prone to dental caries. However, genetic predisposition does not override the importance of good oral hygiene and regular dental care.
Cavities and Bad Breath
Cavities can indeed cause bad breath, also known as halitosis. When cavities develop, bacteria in the mouth feed on food particles left on or between teeth. This bacterial activity produces foul-smelling gases, leading to bad breath. Addressing cavities can help improve oral odor.
Preventing Dental Caries
Preventing dental caries is essential for maintaining good oral health. Several key strategies can help reduce the risk of cavities:
- Oral Hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles that can contribute to cavity formation.
- Dietary Choices: Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks can reduce the exposure of your teeth to substances that promote decay.
- Fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel. Fluoridated toothpaste, mouthwash, and professional fluoride treatments can help protect your teeth.
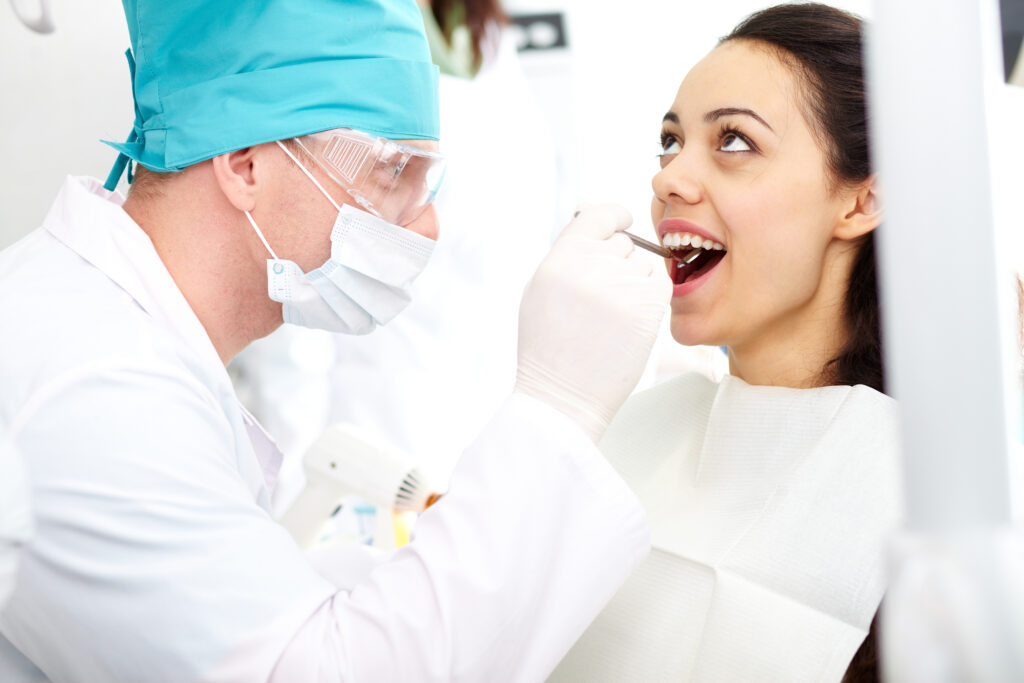
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings allows for the early detection and treatment of cavities.
Treatment for Cavities
The treatment for cavities depends on the extent of the decay. Common treatment options include:
- Dental Fillings: For smaller cavities, dentists can remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill it with materials like composite resin or amalgam.
- Dental Crowns: In cases of extensive decay, a dental crown may be necessary to restore the tooth’s structure and function.
- Root Canal Therapy: When a cavity reaches the tooth’s pulp (nerve) and causes severe infection, a root canal procedure may be required to save the tooth.
The Role of Bacteria in Dental Caries
Dental caries are primarily caused by specific bacteria in the mouth, particularly Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus species. These bacteria metabolize dietary sugars and produce acids, which lead to the demineralization of tooth enamel and the formation of cavities.
Conclusion
Cavities and dental caries are common dental conditions that can impact oral health and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options is vital for maintaining a healthy smile. By practicing good oral hygiene, making informed dietary choices, and seeking regular dental care, you can minimize the risk of cavities and enjoy a lifetime of healthy teeth and gums. If you have concerns about cavities or need personalized guidance, don’t hesitate to consult with a dentist for expert advice and treatment.
FAQs
Can cavities be reversed?
Cavities, also known as dental caries, can be arrested or slowed down but typically cannot be completely reversed once tooth enamel has been damaged. Early-stage cavities can be remineralized through fluoride treatments and good oral hygiene practices. However, once a cavity has progressed and caused significant enamel loss, it usually requires dental treatment, such as a filling or crown, to restore the tooth.
Can cavities cause headaches?
Cavities themselves do not directly cause headaches. However, if a cavity progresses and leads to a dental infection or abscess, it can cause localized pain in the affected tooth and surrounding areas, which may result in headaches in some cases due to the proximity of nerves and blood vessels.
Can cavities go away on their own?
Cavities do not go away on their own. They require dental intervention to prevent further decay and restore the affected tooth’s structure. Early-stage cavities might be halted or remineralized through good oral hygiene and fluoride use, but dental treatment is usually necessary to repair the damage.
Can cavities stop growing?
With proper dental care, including regular check-ups and maintenance of good oral hygiene practices, cavities can be stopped from progressing. Fluoride treatments and dental fillings are commonly used to prevent cavities from growing larger.
Can cavities be removed by brushing?
Cavities cannot be removed by brushing alone. While brushing and flossing are essential for preventing cavities, once they have formed, professional dental treatment is necessary to remove the decayed tooth structure and restore the tooth with a filling or other appropriate treatment.
Can cavities cause bad breath?
Yes, cavities can cause bad breath. When cavities develop, bacteria in the mouth can break down food particles left on or between teeth, producing foul-smelling gases and leading to bad breath (halitosis).
Can cavities heal on their own?
Cavities cannot heal on their own. Dental caries is a progressive condition, and without intervention, it will continue to worsen over time. Early intervention by a dentist is essential to stop the decay and preserve the affected tooth.
Can cavities be genetic?
Genetics can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to cavities. Some people may have genetically determined factors that make them more prone to dental caries, such as the composition of their saliva and the structure of their teeth. However, proper oral hygiene and dental care can still help prevent cavities, regardless of genetic predisposition.
Can cavities spread?
Cavities can spread if left untreated. The decay can advance deeper into the tooth and potentially affect neighboring teeth if the bacteria causing the cavity are not removed or if oral hygiene is inadequate.
Can cavities cause jaw pain, ear pain, swollen lymph nodes, or a sore throat?
Advanced cavities or dental infections can lead to localized jaw pain, ear pain, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, or a sore throat due to inflammation and infection spreading to surrounding tissues. It’s important to seek prompt dental care if you experience these symptoms.
Can cavities cause tooth pain?
Yes, cavities can cause tooth pain. As the decay progresses and approaches the tooth’s nerve, it can result in sensitivity and sharp or throbbing pain. This pain is a sign that the cavity has advanced and requires dental treatment.
Can cavities cause cancer or migraines?
Cavities themselves do not cause cancer or migraines. However, untreated dental infections or severe dental problems may contribute to overall health issues or headaches in some cases. It’s essential to address dental issues promptly to prevent complications.
Can cavities be spread by kissing?
Cavities are not directly spread through kissing. However, sharing oral bacteria with someone who has cavities may increase the risk of developing cavities, especially if both individuals have poor oral hygiene practices.
How are cavities treated?
The treatment for cavities typically involves removing the decayed tooth structure and filling the cavity with a restorative material like composite resin, amalgam, or a dental crown in more severe cases. The choice of treatment depends on the extent of the decay and the dentist’s recommendation.
What causes tooth decay?
Tooth decay is primarily caused by the interaction of bacteria in the mouth with sugars and carbohydrates from food and drinks, resulting in the production of acids that erode tooth enamel over time.
What is dental caries?
Dental caries is another term for tooth decay or cavities. It refers to the process of tooth enamel demineralization and decay caused by acid-producing bacteria in the mouth.
How to prevent dental caries?
Preventing dental caries involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks, getting fluoride treatments, and visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings.
What causes dental caries?
Dental caries is primarily caused by specific bacteria in the mouth, particularly Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus species, which metabolize sugars and produce acids that erode tooth enamel.
How does dental decay start?
Dental decay starts when acids produced by oral bacteria dissolve the minerals in tooth enamel, leading to the formation of cavities or caries.
What is the role of bacteria in dental caries?
Bacteria play a crucial role in dental caries by metabolizing sugars and producing acids that demineralize tooth enamel, leading to cavity formation.
How long does it take for a cavity to start forming?
The time it takes for a cavity to form can vary depending on factors like oral hygiene, diet, and individual susceptibility. It can take several months to years for a cavity to develop fully.
Are cavities contagious?
Cavities themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause cavities can be transmitted through activities like sharing utensils, kissing, or close contact, potentially increasing the risk of cavities in others.
How to remove tooth decay yourself?
Attempting to remove tooth decay at home is not recommended. Dental decay removal requires professional skills and equipment. Home remedies cannot effectively address the problem and may worsen the condition.
What causes tooth decay class 10?
Tooth decay is primarily caused by the interaction of oral bacteria with dietary sugars and carbohydrates, leading to acid production and enamel erosion.
Pathophysiology of dental caries:
The pathophysiology of dental caries involves a complex process where acids produced by bacteria lead to demineralization of tooth enamel, eventually resulting in the formation of cavities.